Cycling’s impact on men’s sexual health is hardly news, and cycling exposes women to the same problem. Gynecologist Luc Baeyons found in his survey that 60% of female cyclists in his sample had experienced genital problems such as perineal numbness, skin infections, chronic swelling, and lymph node damage.
Traditional saddles are too tight
When riding a bicycle, there are three main parts of the body that come into contact with the bike: hands, feet, and sitting bones. Conventional bicycle saddles are usually flat in the upper part and slightly raised in the middle. The purpose of this design is to better fit the angle of the pelvic floor of the human body so that the weight of the body is evenly distributed on the saddle. However, this “seamless fit” design will cause the compression of blood vessels and nerves in the male genitals, which will increase the risk of sexual dysfunction in the long run. And for women who don’t have that lump under the crotch, this design doesn’t seem so reasonable – the blood vessels and nerves in the genitals are also compressed, causing numbness and tingling.
How about a saddle with a slot in the middle?
It makes room for the testicles in men to distribute pressure on the ischium. Does it same apply to women? This doesn’t seem to be very effective – Dr. Steven Schrader found that using such a saddle puts more pressure on the perineum and increases the chance of stinging. And Dr. Eabric Bressel of Utah State University believes that this is because the saddle with a groove in the middle increases the angle of the pelvic floor forward tilt.

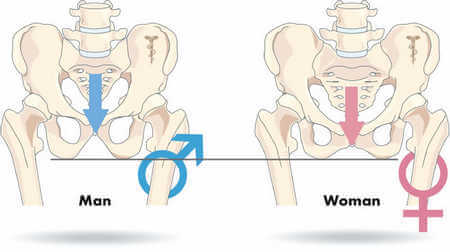
The included angle of the pelvic floor is slightly larger in women than in men. This results in some male saddle not properly supporting the female ischial bones and instead concentrates the weight of the body on the perineum. Therefore, choosing a wider saddle can have the effect of reducing the pressure on the perineum, allowing the pressure to fall correctly on the sitting bones.
Handlebar height is the main reason
Lowering the handlebars and leaning over is indeed more aerodynamic, allowing you to ride faster and with less effort, but at the cost of putting more pressure on the perineum.
Researchers from Yale University looked at 48 women who cycled regularly and covered at least 16km a week. 62% of them said they had experienced perineal numbness, tingling, or pain in the last month. The researchers recorded the height of the participants’ bicycle handlebars relative to the saddle, asked them to bring their bicycles or saddles to the laboratory, and asked them to ride in their preferred position. After reaching equilibrium, they recorded the pressure on the saddle. In addition, the sensitivity is also examined by detecting the perineal vibration perception threshold (I am curious about what this experimental equipment is, whether it is dedicated for research or for daily use…).
It was found that the lower the relative position of the handlebar, the higher the pressure on the middle perineum. It is presumed that the reason is the distance between the middle of the perineum and the ischium is too far, and the pressure cannot be distributed to the ischial bones well. At the same time, the vibration perception threshold survey results showed that the handlebars that are too low can increase the pudendal vibration perception threshold, that is, reduce nerve sensitivity – in fact, this reduction in sensitivity is not uniform (the anterior vagina and the left labia are more reduced many). This may be caused by people’s habit of putting stress on one side of the body.
It is most effective to straighten the body
Also due to the difference in the angle of the pelvic floor, women tended to have a greater anteversion of the pelvic floor and increased perineal pressure when using bicycles with the same handlebar height. Therefore, it is most effective to adjust the height of the handlebars, reduce the forward tilt of the pelvic floor, and distribute the weight of the body on the ischium, not on the perineum!
But that’s not realistic for speed-seeking female cyclists. Although there is a lack of targeted experimental evidence, Dr. Schreider believes that a noseless saddles for men should also be a good choice for women. However, it should be noted that noseless saddles may reduce the handling of the car.

In fact, cycling is a wonderful sport, it is not necessary to give up eating for fear of affecting sexual health. The important thing is to choose the frame size that suits you, choose the saddle according to your seat bone width, and adjust thesaddle to the appropriate height under the guidance of experts. In addition, I have to remind you, don’t assume you can pedal. Proper cycling takes practice, the correct cycling posture also needs to be practiced frequently. Correct cycling position and timely shifting will allow you to evenly distribute your weight to your arms, legs and hips, which on the one hand can effectively convert physical strength into the power of the bike, and more importantly, reduce the pressure on the perineum. In addition, a good cycling pants is also essential for long-distance cycling. Of course, the easiest and most economical way is to get down and move around every now and then during your cyling.
